- Home
- OUR SERVICES
- Pay Now
- About Us
- Contact
Received an income tax certificate? Then submit your tax return now. Get Started Now
- Home
- OUR SERVICES
- Pay Now
- About Us
- Contact
Don’t stress or worry about last-minute ITR filling. Trust our expert –
NGO Registration Online India
- Expert assistance to choose the right structure
- India’s best lawyers draft your Deed/Bylaws/MOA
- Seamless online process at the lowest price
Get Free Consultation
HOW WE WORK
Working Process

Get Started, Incorporate
Your Business in India.

Expert Advisors available
to answer your
questions

A large pool of CA,CS &
Lawyers (All Over India)

We serve all sectors and
Industries (Scalable)
HOW WE WORK
Right plan for your business
- TRUST & SOCIETY
- SECTION 8 COMPANY
Standard
₹4999 + GOVT FEE
It offers a reliable and cost-effective hosting solution with all the essentials you need to get started.
- Expert Assisted Process
- On Call Consultation
- Draft Deed Preparation
- PAN
Additional Feature:
*Notes
Startup Plan
₹9499 + GOVT FEE
It includes a range of advanced features and resources to support and grow your online presence.
- CA/CS Assisted Process
- On Call Consultation
- Draft Deed/MOA & By-Laws Preparation
- PAN
- 12A Registration
- 80G Registration
Additional Feature:
*Notes
Shark Plan
₹14999 + GOVT FEE
It offers the most robust set of features and resources to ensure the smooth operation and growth of your website.
- CA/CS Assisted Process
- On Call Consultation
- Draft Deed/MOA & By-Laws Preparation
- PAN
- 12A Registration
- 80G Registration
- Darpan Registration
- CSR-1 Registration
- Financial Reports Preparation (Upto 300 Transactions)
- Income Tax Filing
Additional Feature:
*Notes
Standard
₹4999 + GOVT FEE
It offers a reliable and cost-effective hosting solution with all the essentials you need to get started.
- Expert Assisted Process
- Name Reservation in 2 days
- Digital Signature Certificates in 48 Hours
- Director Identification Number for Directors
- NGO Application Form Filing in 5 Days
- Drafting e-MOA & e-AOA
- ePAN & eTAN
- Section 8 License
Additional Feature:
*Notes
Startup Plan
₹11999 + GOVT FEE
It includes a range of advanced features and resources to support and grow your online presence.
- CA/CS Assisted Process
- On Call Consultation
- Name Reservation in 2 days
- Digital Signature Certificates in 48 Hours
- Director Identification Number for Directors
- NGO Application Form Filing in 5 Days
- Drafting e-MOA & e-AOA
- ePAN & eTAN
- Section 8 License
- 12A Registration
- 80G Registration
- CSR-1 Registration
Additional Feature:
*Notes
Shark Plan
₹14999 + GOVT FEE
It offers the most robust set of features and resources to ensure the smooth operation and growth of your website.
- CA/CS Assisted Process
- On Call Consultation
- Name Reservation in 2 days
- Digital Signature Certificates in 48 Hours
- Director Identification Number for Directors
- NGO Application Form Filing in 5 Days
- Drafting e-MOA & e-AOA
- ePAN & eTAN
- Section 8 License
- 12A Registration
- 80G Registration
- Darpan Registration
- CSR-1 Registration
- Financial Reports Preparation (Upto 300 Transactions)
- Income Tax Filing
Additional Feature:
*Notes

Not sure about the packages?
Talk to our experts to understand your business compliance
needs and suggest the best plan for you.
needs and suggest the best plan for you.
2A Registration & 80G Registration
₹7999/-
- Expert Assisted Process
- Documents Preparation
- 12A & 80G Application Filing
NGO Darpan Registration
₹1999/-
- Expert Assisted Process
- Documents Preparation
- NGO Darpan Registration
CSR-1
Registration
₹1999/-
- Expert Assisted Process
- Documents Preparation
- CSR-1 Registration
FCRA
Registration
₹4999/-
- Expert Assisted Process
- Documents Preparation
- FCRA Registration
- Types of NGO Registration
- Understanding the Difference
- Documents Required for NGO Registration
- Benefits
- Process of Section 8 Company Registration
- Government Grants & Exemptions
- Why TaxSharks
- FAQ’s
What are the Types of NGO Registration in India?
There are three types of NGOs widely registered in India.
Trust
Trust registration refers to the process of legally establishing a trust in India. A trust is a form of non-profit organisation (NPO) that is created to provide assistance and support to specific causes, such as education, health care, and community development. The trust registration process is governed by the Indian Trusts Act, 1882, and is typically handled by a team of legal experts and professionals.
Society
Society registration refers to the process of forming a society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860. A society is a group of individuals who come together to achieve a common goal or objective. Societies are formed to promote charitable, religious, educational, scientific, literary, or social causes.
Section 8 Company
Section 8 Company is a type of non-profit organisation that is registered under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013. It is registered with the sole purpose of promoting commerce, art, science, religion, charity or any other useful object, and not for the purpose of making a profit. This type of company is also known as a Non-Profit Organisation or Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO).
Difference Between - Trust, Society & Section 8 Company
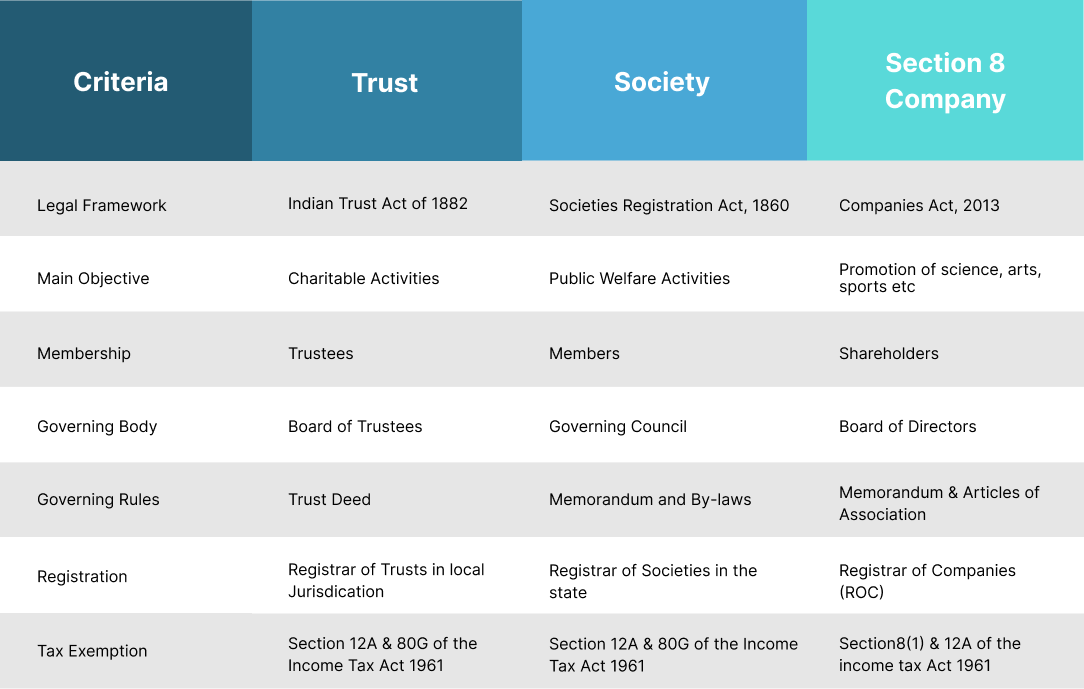
Trust & Society Registration
Once the payment for the registration is done, it takes about 10 to 15 days for online registration to be completed under the Indian Trust Act – 1882. Before the deed becomes valid throughout the country, the settler has to deliver a presentation at the registrar’s office. Note: On the scheduled date for registration, the Author of the Trust shall be present in the Register Office for registration
List Documents For Company Registration
As experienced consultants for company registration, we at Setindiabiz understand the importance of documentation in ensuring a smooth and successful registration process for a Private Limited Company. To make it easier for our clients, we have compiled a table below listing all the necessary documents required for the incorporation process.
Director & Shareholders Documents
- Passport size colour photo
- PAN Card (Mandatory)
- Proof of Identity (any one of the below)
- Passport
- Aadhar Card
- Driving License
- Voter ID
- Proof of Residence (Any one of the below)
- Bank Statement
- Electricity Bill
- Gas Bill
- Telephone Bill
- Mobile Bill
Proof of Registered Office Address
- Proof of Property Ownership
- Electricity Bill
- Gas Bill
- Telephone Bill
- Mobile Bill
- NOC from the Owner of Premises
Note: Address proof for the promoter and registered office premises should not be older than two months and must contain the full address and owner name.

Company Name Check
Choosing a unique name for your company in compliance with name availability guidelines that don’t clash with any existing companies, LLPs, or trademarks
Get Digital Signatures
Creating the Digital Signature (DSC) for all the directors as well as shareholders.
Draft MOA, AOA, & Declarations
Prepare the Memorandum (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA) detailing legal and internal rules and draft a few declarations as per the Companies Act. We are here to help.
ROC Filing for Incorporation
Finally, Submit the Spice Plus Form to ROC with directors/shareholders’ DSC, along with the promoter’s documents and proof of registered address for incorporation.
12A Registration
Section 12A Registration is an registration through which a NGO can get Exemption from the Income Tax Department in India.
NGOs registered under Section 12A do not have to pay income tax since they are registered for the welfare of the Society they are eligible to claim exemptions.
And since 12A Registration Online is legally recognised evidence of your NGO’s existence, it is helpful in obtaining validation from foreign governments and organisations.
NGOs registered under Section 12A do not have to pay income tax since they are registered for the welfare of the Society they are eligible to claim exemptions.
And since 12A Registration Online is legally recognised evidence of your NGO’s existence, it is helpful in obtaining validation from foreign governments and organisations.
80G Registration
The Income Tax Department grants an 80G Certificate to a non-profit organisation. Section 80G of the Income Tax Act provides tax benefits to donors who contribute to specified funds, charities, or institutions.
Donors making contributions to trusts, institutions, or funds approved under Section 80G can claim deductions on their taxable income. This encourages philanthropy and charitable giving. Donors can claim either a 100% or 50% deduction, depending on the nature of the recipient entity.
Section 12A facilitates the tax-exempt status of charitable or religious trusts, while Section 80G encourages donations to such entities by providing tax benefits to donors. Both sections play integral roles in promoting and sustaining philanthropic activities in India.
Donors making contributions to trusts, institutions, or funds approved under Section 80G can claim deductions on their taxable income. This encourages philanthropy and charitable giving. Donors can claim either a 100% or 50% deduction, depending on the nature of the recipient entity.
Section 12A facilitates the tax-exempt status of charitable or religious trusts, while Section 80G encourages donations to such entities by providing tax benefits to donors. Both sections play integral roles in promoting and sustaining philanthropic activities in India.
NGO Darpan Registration
NGO Darpan is as an online platform developed by NITI Aayog. Its inception dates back to 2015 when the Indian Government introduced this initiative. This digital portal functions as a centralized national database dedicated to cataloging NGOs and voluntary organizations in India. Each NGO operating in the country is required to undergo registration on this portal, providing self-declared information encompassing their activities, projects, and sources of income. The main objective behind creation of the Darpan Portal is to facilitate NGOs in receiving Government grants and funding easily using their Unique Darpan registration ID. The information curated on this platform is made publicly accessible, enabling the government and other stakeholders to gain insights into the functioning and impact of registered NGOs.
CSR-1 Registration
CSR stands for Corporate Social Responsibility, and it is a concept that is increasingly being adopted by businesses around the world. CSR is all about businesses taking responsibility for their impact on society and the environment, and taking action to improve things.
As per CSR Rules every company with a net worth of ₹500 crore or more, or turnover of ₹1,000 crore or more are required to spend 2% of their average net profits from the previous three financial years on CSR activities.
If you are an NGO that works on social or environmental projects, then you may be able to receive funding from companies that are required to spend money on CSR activities. This can be a great way to get additional funding for your work.
As per CSR Rules every company with a net worth of ₹500 crore or more, or turnover of ₹1,000 crore or more are required to spend 2% of their average net profits from the previous three financial years on CSR activities.
If you are an NGO that works on social or environmental projects, then you may be able to receive funding from companies that are required to spend money on CSR activities. This can be a great way to get additional funding for your work.
FCRA Registration
The FCRA registration stands for registration under Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 which regulates the acceptance and utilisation of foreign contributions and hospitality by organisations and individuals.
The FCRA registration is a prerequisite for any association or non-profit organisation in India seeking foreign donations or contributions.
01. What are the different types of NGO registration available in India?
In India, NGOs can be registered under three main categories:
Trust: Governed by the Indian Trusts Act, 1882. Suitable for public charitable trusts.
Society: Governed by the Societies Registration Act, 1860. Suitable for organizations working for the promotion of literature, science, or fine arts.
Section 8 Company: Governed by the Companies Act, 2013. Suitable for non-profit organizations intending to promote commerce, art, science, sports, education, research, social welfare, religion, charity, protection of environment or any such other object.
02. What are the basic requirements for registering an NGO as a Trust?
To register an NGO as a Trust, the following requirements must be met:
Trust Deed: A legal document that needs to be drafted on a non-judicial stamp paper.
Trustees: Minimum of two trustees are required.
Property/Assets: Details of the property or assets to be transferred to the Trust.
Registration: The Trust Deed needs to be registered with the local Registrar.
03. What documents are needed for registering an NGO as a Society?
The essential documents required for registering a Society include:
Memorandum of Association (MoA): Stating the society's name, objectives, names, addresses, and occupations of the governing body members.
Rules and Regulations: Outlining the functioning and management of the Society.
Governing Body: Minimum of seven members.
Address Proof: Registered office address proof.
Identity Proof: Identity proofs of all members of the governing body.
04. What are the steps to register a Section 8 Company?
The steps to register a Section 8 Company are as follows:
Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): For all proposed directors.
Director Identification Number (DIN): Apply for DIN for the proposed directors.
Name Approval: File for name approval with the Registrar of Companies (RoC).
File Incorporation Forms: Submit forms INC-12 (for license), SPICe (INC-32), e-MoA (INC-33), and e-AoA (INC-34) along with necessary documents.
Issuance of License: After verification, RoC issues a license under Section 8.
Incorporation Certificate: Upon issuance of the license, an incorporation certificate is provided.
05. What are the benefits of registering an NGO in India?
Registering an NGO in India offers several benefits:
Legal Recognition: Provides a legal identity to the organization, making it easier to enter into contracts and agreements.
Tax Exemption: Eligibility to apply for income tax exemptions under Section 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act.
Funding Opportunities: Access to government grants, foreign donations (subject to FCRA compliance), and other funding options.
Credibility and Trust: Enhances the credibility of the organization in the eyes of donors, beneficiaries, and government authorities.
Perpetual Succession: The NGO continues to exist even if there are changes in membership or trustees.
